Uncover the Reasons Behind Google’s ‘Crawled – Currently Not Indexed’ Status and Learn Effective Solutions to Ensure Your Pages Get Indexed and Visible in Search Results
Currently not indexed’ error in Google Search Console. Uncover the reasons behind the ‘Crawled – Currently not indexed’ error in Google Search Console and solutions to get your pages indexed.
Imagine you’re hosting a grand opening event for a new store. You’ve sent out invitations, put up signs, and ensured everything inside is perfect. The decorations are up, the shelves are stocked, and you’re ready for customers.
However, there’s a problem—the main door is locked, and the welcome sign is hidden behind some bushes. People walk by but can’t find the entrance, so they keep moving.
This happens when your web page faces the ‘Crawled – Currently Not Indexed’ error in Google Search Console. Your page is live, and Google has seen it, but it’s like that locked door—users can’t access it through search because it’s not in the index.
Just like you would fix the entrance to your store to welcome customers, you must address this error to ensure your audience can find and access your valuable content.
Overview of the Issue

The ‘Crawled – Currently Not Indexed’ error in Google Search Console is a frustrating roadblock for many website owners and SEO professionals.
This status indicates that Google has crawled your webpage but has decided not to include it in its index. This situation can be puzzling because your content is inaccessible to users via Google’s search results, directly affecting your website’s visibility and potential traffic.
Importance of Indexing
Indexing is critical to search engine optimization (SEO). When a page is indexed, it becomes part of Google’s searchable database, meaning it can appear in search results when relevant queries are made.
If a page is not indexed, it essentially doesn’t exist in the eyes of Google users, no matter how valuable the content may be. Ensuring your pages are indexed is crucial for driving organic traffic, improving search rankings, and achieving your website’s goals.
2. Understanding the ‘Crawled – Currently Not Indexed’ Error

Definition: The ‘Crawled – Currently Not Indexed’ status in Google Search Console refers to pages that Google’s crawlers have accessed and reviewed but have not been added to the search index. This means that although Google knows the page’s existence, it has decided, at least temporarily, not to include it in its search results.
Common Causes:
- Content Quality: One of the most common reasons a page needs to be indexed is low-quality content. Google prioritizes informative, well-written content that provides value to the user. Thin content—pages with very little text or low informational value—often fails to meet Google’s quality standards, leading to non-indexing.
- Duplicate Content: Pages containing content identical or similar to other pages on your site or across the web can be flagged as duplicates. Google aims to give users diverse, original content in its search results. If your page offers nothing new or unique, it may not be indexed.
- Technical Issues: Various technical problems can prevent a page from being indexed. Server errors, like a 5xx status code, can block crawlers from accessing your content. Slow loading times might cause Google to abandon the crawl before it finishes. Incorrect use of meta tags like noindex or directives in the robots.txt file can inadvertently block indexing.
- Google’s Discretion: Sometimes, Google may choose not to index a page based on its algorithms and judgment. This decision could be influenced by factors such as the page’s perceived importance, the overall quality of the site, or a comparison with similar content across the web.
3. How to Identify the Problem

Using Google Search Console
Google Search Console is your primary tool for identifying and diagnosing the ‘Crawled – Currently Not Indexed’ issue.
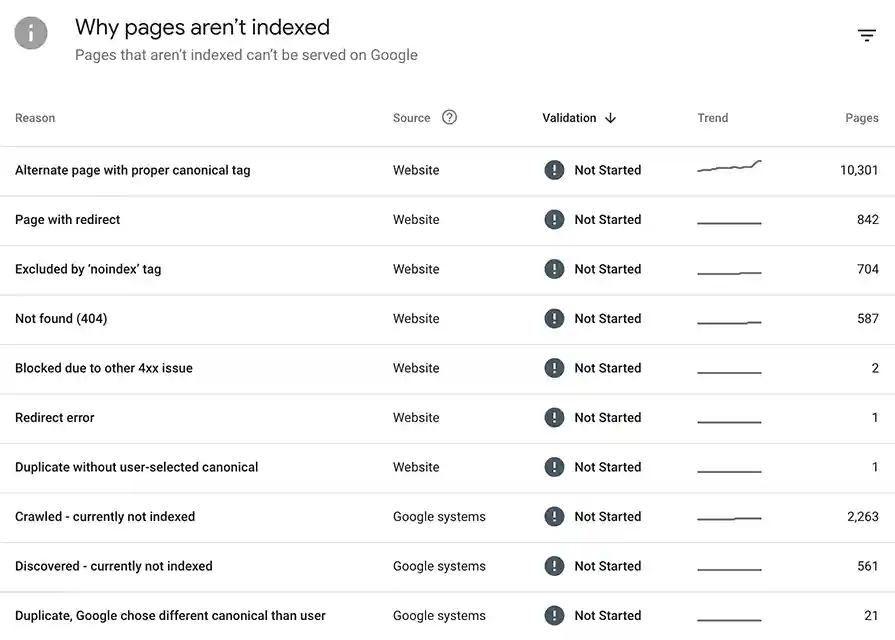
To find affected pages, navigate to the Coverage report and filter for the ‘Crawled – Currently Not Indexed’ status.
This report will list all URLs that Google has crawled but not indexed, giving you a starting point for further investigation.
Analyzing Crawl Reports
Once you’ve identified the affected pages, delve deeper into the crawl reports Google Search Console provides.
Check for any warnings or errors associated with these pages. Look for patterns that might indicate common issues, such as similar content types or specific sections of your website being affected.
Manual Checks
In addition to automated reporting, manual checks are performed on the affected URLs. Search for the URL in Google using the ‘site:’ operator (e.g., site:example.com/page-URL) to see if it’s indexed. Also, visit the page directly to check for any obvious errors, such as slow loading times, server issues, or content that might be considered low quality.
4. Solutions to Fix the Error
Improve Content Quality:
- Expand Thin Content: Pages with thin content often fail to meet Google’s quality standards. To fix this, add more valuable information to these pages. This could include expanding the text with detailed explanations, adding images, videos, or infographics, and ensuring the content fully addresses the user’s intent.
- Address Duplicate Content: Duplicate content can confuse search engines and reduce the likelihood of your pages being indexed. Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of a page when similar content exists. Ensure each page on your site offers unique value, whether through different content, targeting different keywords, or serving a different user intent.
Technical Fixes:
- Resolve Server Errors: Server issues like 5xx errors can prevent Google from accessing your page. Use tools like Google Search Console’s Crawl Stats report or server logs to identify these errors. Work with your hosting provider to ensure your server is reliable and responsive, and consider using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to improve performance.
- Optimize Page Load Times: Slow page load times can cause crawlers to give up before a page is fully loaded, leading to indexing issues. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or Lighthouse to identify areas for improvement. Optimize images, minify CSS and JavaScript, and leverage browser caching to reduce load times.
- Correct Directives: Incorrect use of meta tags or robots.txt can inadvertently block Google from indexing your pages. Double-check that your pages are not set to noindex unless intentional, and ensure your robots.txt file is correctly configured to allow Googlebot to crawl and index your site.
Request Indexing:
- Using Google Search Console: If you’ve improved a page and want to request a re-crawl, use the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console. Enter the URL and click ‘Request Indexing.’ Google will prioritize the page for crawling and potential indexing.
Build Internal Links: Increasing the number of internal links pointing to the affected page can help Google find and prioritize it for indexing. Link to the page from relevant, high-traffic areas of your site, and ensure the anchor text is descriptive and related to the page’s content.
5. Preventative Measures
Regular Audits
Conduct regular audits of your website to avoid indexing issues in the future. Use Google Search Console to monitor crawl errors, index coverage, and any issues with specific pages. Regular audits will help you catch problems early before they impact your site’s visibility.
Content Strategy
Develop a strategy that creates high-quality, unique, and valuable content. This strategy should include thorough keyword research, understanding user intent, and regularly updating content to keep it relevant and fresh. A strong content strategy reduces the risk of producing low-quality or duplicate content that might not be indexed.
Technical SEO Best Practices
Implement ongoing technical SEO practices to ensure your site remains healthy and indexable. This includes maintaining a clean and organized site structure, ensuring fast load times, and regularly checking for and fixing any crawl errors or server issues.
Conclusion
Recap: Addressing the ‘Crawled – Currently Not Indexed’ error is essential for ensuring your website’s content is accessible to users through Google’s search results. By understanding the common causes, identifying the specific issues affecting your pages, and applying the appropriate fixes, you can improve your chances of getting your pages indexed.
Proactive monitoring and consistent improvements to your website’s content and technical health are key to maintaining good standing with Google’s indexing processes.
Regular audits, a strong content strategy, and adherence to technical SEO best practices will help you avoid future indexing issues and ensure your site continues to attract and engage users.
7. Additional Resources
Links to Google Documentation:
SEO Tools:

