What is a product life cycle analysis and management
Learn about product life cycle analysis and management.
Product life cycle management and analysis is a process businesses use to understand their products’ different stages and the whole product lifecycle stages.
I left my two-year job with IBM and landed my first product manager job with the railroad. On my first day, I was introduced to processes and pricing models for freight.
So when I saw rows and rows of 5 draw file cabinets with no database, you can guess what I did. We reduce pricing cycle times from 3-5 days to 5 minutes with the traffic manager on the phone.
- What is the product life cycle and its management?
- What are the 5 stages of a product life cycle?
- What are the 5 steps of PLM?
- What is product lifecycle management (PLM)?
Ever write a check (yes, people still write checks), and wonder what that machine is they are sending through? Well, we at SORICON invented it in Boulder, CO. That was my product to push out into the multilane stores, c-stores, and more…we were the Verifone of checks then.
Distributed computing and SaaS models in the PLM (product life management), another HP spin-out, required me to reposition and seek additional investor funding with a well-structured roadshow. It was secured, and PTC later bought the company.
I could go on about how I’ve been involved with products and services for over 30 years. My model is simple: add value and always help.
This information can help with marketing decisions, ensuring the product is used to its fullest potential. 10 Most In-Demand Types of SEO Services to Focus On in 2025
Many resources, such as social media, customer service, surveys, focus groups, and competitive digital signals, can help improve a product’s life cycle.
Businesses can drive revenue and profits by using these tools and understanding the different stages of the product life cycle.
Do you want to make your business more successful?

Product life cycle analysis is an important tool for businesses to understand. By knowing which stage of their product’s B2C life cycle their product is in, businesses can make better decisions about their marketing strategies and ensure they make the most of their products. The chief product officer and product marketing managers typically carry out product lifecycle management and product lifecycle strategies.
Many resources are available to help improve the product life cycle, like the customer service department, social posts, surveys, focus groups, and competitive digital signals. With so much information at your fingertips, there’s no reason not to make your business thrive.
Learn more about how product life cycle analysis can benefit your business! What is the product life cycle of a B2B firm?
The product life cycle of a B2B firm is similar to that of a consumer-focused company, but there are some key distinctions.
Products move through different stages as they age; businesses must understand them to make the most of their products. AI Agentic Systems for Marketing Healthcare Organizations
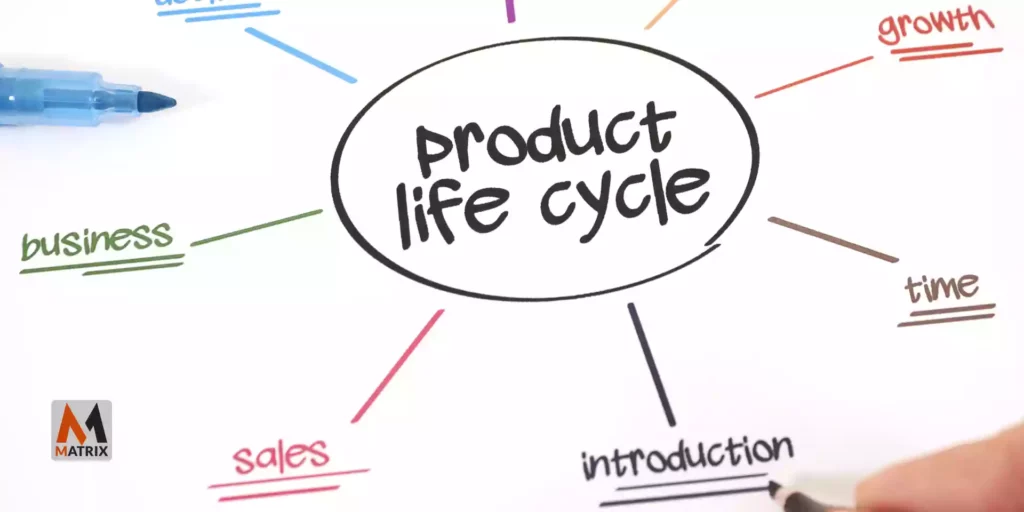
Here are the five stages of the product life cycle:
1. Introduction: This is when the product is first released to the market. The company is trying to generate interest and awareness among consumers.
Your Blueprint for SEO Success in 2025
Whether you’re a business owner, marketer, or seasoned SEO professional, this guide is tailored to give you a competitive edge in the evolving digital landscape. Get SEO Pricing.
2. Growth: The product is starting to catch on with consumers, and sales are increasing. The company is working to sustain this growth and increase its market share.
3. Maturity: The product has peaked in its sales and market share. Competition is fierce, and companies are trying to hold onto their customers.
4. Decline: Sales are dropping, and the product is losing popularity. This stage can be difficult for companies, but there’s still potential for a turnaround if they’re willing to make changes.
5. Retire/End of Life: The product is no longer being made or sold. This stage can come in many forms, depending on the product’s life cycle curve.
Products go through different stages as they age, and businesses must understand them to make the most of their products. Global business use and pair there for better market penetration and competitive advantage.
- Extending product lifecycle
- Product lifecycle analysis tools
By understanding the product life cycle, businesses can generate revenue and profits.
Branch Models: Unlocking Scalable Growth
In the age of digital transformation, marketing managers are constantly seeking innovative ways to stay competitive and relevant. But how? Watch the video!
What is the product life cycle of a B2C firm?
The product life cycle of a B2C firm is similar to that of a B2B firm, but there are some key distinctions.
Products move through different stages as they age; businesses must understand them to make the most of their products.
Sure, here is a summary of the chief marketing officer (CMO) and the product life cycle of a B2C firm:
Chief Marketing Officer (CMO)
A chief marketing officer (CMO) is a corporate executive responsible for an organization’s marketing activities. The CMO’s primary responsibility is to generate revenue by increasing sales through effective marketing strategies. They oversee various aspects of marketing, including:
- Brand management: Developing and maintaining a strong brand identity that resonates with the target audience.
- Marketing communications: Creating and executing marketing campaigns across various channels, such as advertising, public relations, and social media.
- Market research: Analyzing market trends and customer behavior to inform marketing decisions.
- Product marketing: Developing and positioning products to meet customer needs and maximize sales.
- Distribution channel management: Ensuring products are available to customers through the right channels.
- Pricing: Developing pricing strategies that are competitive and profitable.
- Customer success: Ensuring customers are satisfied with the products and services they receive.
The CMO’s role is becoming increasingly important as businesses compete in a globalized and digital marketplace. Effective marketing can help businesses increase brand awareness, generate leads, and drive sales.
The product life cycle (PLC) is a framework that describes a product’s stages, from its introduction to its decline and eventual removal from the market. The PLC is typically divided into four stages:
- Introduction: This is the stage where the product is first introduced to the market. Sales are typically low, and the company is focused on building awareness and generating interest.
- Growth: This is the stage where the product gains popularity and sales grow. The company’s focus shifts to expanding distribution and maximizing market share.
- Maturity is the stage where the product reaches its peak sales. At this stage, the company focuses on maintaining market share and defending against competitors.
- Decline: This is when sales decline due to market saturation, new product competition, or changing consumer preferences. The company may consider reducing marketing efforts or discontinuing the product.
The PLC is a useful tool for businesses to understand the different stages of a product’s life and develop appropriate marketing strategies for each stage. For example, a company in the introduction stage of the PLC would focus on creating awareness and generating interest. In contrast, a company in the maturity stage would focus on maintaining market share and defending against competitors.
Here is a table summarizing the key characteristics of each stage of the PLC:
| Stage | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Low sales, high marketing costs, focus on building awareness |
| Growth | Increasing sales, expanding distribution, focus on maximizing market share |
| Maturity | Declining sales, reduced marketing efforts, consider discontinuing the product |
| Decline | Declining sales, reduced marketing efforts, consider discontinuing product |
The PLC is not a rigid model, and the length of each stage can vary depending on the product and the market. However, it can be a helpful tool for businesses to understand the challenges and opportunities of each stage and develop effective marketing strategies.
5 steps for product life cycle analysis
1. Know your product: The first step is understanding your product clearly. What are its features? How does it differ from similar products on the market? What are its strengths and weaknesses? This information will be crucial as you move through the different stages of the product life cycle.
2. Understand your market: It’s also important to understand your target market well. Who are your customers? What do they want and need? What are their buying habits? This information will help you decide how to market and sell your product.
3. Monitor sales: Monitor your product’s sales figures. This will help you understand how well the product is doing in the market and identify any changes that need to be made.
4. Evaluate your marketing efforts: Evaluate the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns. Are you reaching your target market? Are customers responding to your messages? If not, it may be time to change your marketing strategy.
5. Make adjustments: As the product life cycle progresses, you must adjust your plans. This could include your marketing strategy, sales approach, or product changes. It’s important to be flexible and willing to make changes as needed.
By understanding product life cycle management, businesses can generate revenue and profits.
Click this article to learn how product life cycle analysis can benefit your business! Digital Marketing for Solar Companies to Increase Sales
Major pain points of managing the product life cycle
The major pain points of managing the product life cycle are understanding when to make changes, gathering customer feedback, and dealing with competition.
If you make changes too early, you may alienate customers. If you make changes too late, you may miss potential profits. It’s a delicate balancing act that requires a lot of finesse.
Another challenge businesses face is gathering customer feedback. This feedback can improve the product life cycle, but getting accurate customer information is difficult. You must be sure you’re getting feedback from the right people and interpreting it correctly.
Finally, businesses have to deal with competition. With so much online information, standing out cannot be easy. You must be sure your product is differentiated from the competition and use the best marketing techniques possible.
These are just a few major pain points of managing the product life cycle. By understanding these pain points, you can better position yourself to succeed.
What is product life cycle analysis?
Product life cycle analysis is the process of examining a product’s lifespan and understanding its different stages.
This information can help you make better decisions about marketing and selling the product.
The different stages of the product life cycle and what that means for businesses
Businesses need to understand their products’ life cycle, which is the cycle from their creation to discontinuation.
Understanding the different stages of the product life cycle can greatly impact businesses.
The first stage of the product life cycle is development. Businesses must decide if there is a market for the product and how it will differ from what’s already available. They also need to determine what the product will cost and how it will be manufactured.
The next stage is launch. Businesses must ensure a good marketing strategy so people know about the product. They also need to ensure enough stock is available and meets demand.
The third stage is growth. Businesses need to continue their marketing efforts and ensure enough stock is available. They may also want to start considering introducing new product versions.
The fourth stage is maturity. The product is no longer new; sales have started to level off. Businesses need to maintain their market share and ensure they’re still profitable, and they may also want to introduce new products.
Unlock Your Website’s Full Potential with a SEO Fix Program
Even the best websites can struggle without robust SEO. Our $2,500 SEO Quick Fix Package is crafted for businesses that demand fast, measurable results. We start with an in-depth SEO audit to diagnose your site’s performance, then implement five targeted optimizations to boost your rankings and drive more traffic.
The fifth and final stage is decline. Businesses need to reduce their costs to make a profit, and they may also want to discontinue the product.
Businesses must understand product life cycle analysis to improve their products. Different techniques can be used to conduct a product life cycle analysis. Knowing which stage of the cycle your product is currently in is important.
By understanding the product life cycle, businesses can make better decisions about their marketing strategies and ensure they make the most of their products. Resources to improve the product life cycle, like the customer service department, social posts, surveys, focus groups, and competitive digital signals, improve the product life cycle.
A product life cycle analysis will help drive revenue and profits.
Most marketing executives are familiar with the product and product life cycle analysis.
Evaluating the performance of the product portfolio provides management with information to guide product strategies for new products, product modifications, and product elimination.
The strategic analysis of existing products requires tracking the performance of the products in the portfolio.
Marketing management must establish parameters and performance levels to gauge product performance. An information system is needed to manage product demand and cost interrelationships.
A system like a marketing analytics platform measures a particular product’s performance. These systems can help evaluate your products. These systems are essential for both B2B and B2C companies.
The purpose of the tracking system is to maintain a product review process that will spot problem products. Marketing management can use analytic reports to help select a strategy for eliminating the problem.
Corrective actions may include adding new products, reducing costs, improving products, changing marketing strategies, or eliminating products.
I used several methods to perform a strategic analysis of our product portfolio. This paper will discuss the product life cycle, portfolio, and positioning analysis and explain the information used to analyze product performance and identify strategy options.

AIProdPad
Rev Up Your Product Development
The product development process is leveraged by AI driven product management strategies and business applications to create and bring products to market faster.
Product Life Cycle
If you’ve read some of my posts before, you will understand the product life cycle. However, let me explain it again. Before we get too far into the discussion, you must understand the product life cycle.
Products, like people, move through life cycles. The product type or a variant of interest should correspond to a defined market need. Life cycle analysis can also focus on a market segment within a product market.
Sales began when the product was introduced and increased over time. Profits lag behind sales since heavy introductory expenses often exceed sales during the initial stage. Industry sales and profits decline after the product reaches maturity.
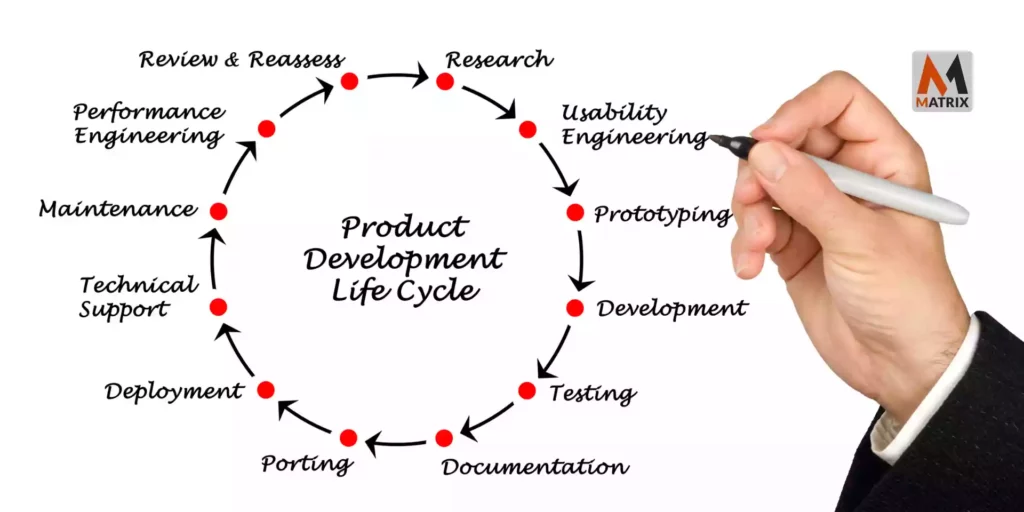
The product life cycle follows an S-shaped curve that portrays a specific product’s sales history. The curve is typically divided into four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline.
- Introduction Stage. It has slow sales growth as the product is introduced to the market. Early adopters are the first to buy. Profits are inconsistent at this stage.
- Growth Stage. This stage shows rapid market acceptance and profit improvement.
- Maturity Stage. Sales growth slowed during this period because most potential buyers accepted the product. Profits stabilized or declined due to increased marketing outlays to defend the product against the competition.
- Decline Stage. The period when sales show a downward trend and profits decline.
Product lifecycle case studies
Apple: Apple is known for its innovative products and ability to create demand for new products even before release. The company has a strong track record of identifying and addressing customer needs and is not afraid to take risks and disrupt existing markets.
Apple’s biggest challenge is staying ahead of the competition and maintaining its reputation for innovation. The company has also been criticized for its high prices and reliance on contract manufacturing.
Apple continues to invest heavily in research and development and has a strong track record of attracting and retaining top talent. The company also has a loyal customer base willing to pay a premium for its products.
Amazon: Amazon is a master of e-commerce, revolutionizing how people shop. The company has a vast network of warehouses and delivery systems, and it can offer a wide selection of products at competitive prices. Amazon is also constantly innovating, and it has developed several successful new products and services, such as Amazon Prime and Amazon Web Services.
Amazon’s biggest challenge is maintaining its growth trajectory. The company also faces increasing competition from other e-commerce giants, such as Alibaba and Walmart.
Amazon is expanding into new markets, such as India, and it continues developing new products and services. The company is also investing heavily in its logistics infrastructure, which will help it improve its delivery times and reduce its costs.
Nike is a leading global athletic footwear and apparel company with a strong brand identity and a loyal customer base. Nike is also known for its innovative products and its commitment to social responsibility.
Nike’s biggest challenge is protecting its brand from counterfeiting. The company also faces increasing competition from other athletic footwear and apparel companies, such as Adidas and Under Armour.
Nike is investing in technology to combat counterfeiting, expanding its product line and international presence, and improving its sustainability practices.
Coca-Cola: Coca-Cola is one of the most recognizable brands in the world. The company has a strong track record of marketing its products effectively and a loyal customer base that enjoys its refreshing taste.
Coca-Cola’s biggest challenge is convincing consumers to drink more soda, as consumption has declined recently. The company also faces increasing competition from other beverage companies, such as Pepsi and Dr Pepper Snapple Group.
- Coca-Cola is expanding its product line to include more healthy and functional beverages. The company also focuses on emerging markets where soda consumption is still growing.
- Procter & Gamble: Procter & Gamble is a global consumer goods company that produces a wide range of personal care and household products. The company has a strong track record of innovation, and it is known for its high-quality products.
Procter & Gamble’s biggest challenge is maintaining its growth trajectory in a slowing global economy. The company is also facing increasing competition from private-label brands.
Procter & Gamble is focusing on developing new products that meet the needs of consumers in emerging markets. The company is also investing in its marketing and distribution capabilities.
These are just a few examples of brands successfully managing their product lifecycles (PLC). By understanding the challenges and opportunities of each stage, companies can develop effective strategies to extend the lifespan of their products and maximize their profitability.
Product Lifecycle Trends to 2025 and Product Lifecycle Challenges
The product lifecycle (PLC) is a framework that describes a product’s stages, from its introduction to its decline and eventual removal from the market. The PLC is typically divided into four stages:
- Introduction: This is the stage where the product is first introduced to the market. Sales are typically low, and the company is focused on building awareness and generating interest.
- Growth: This is the stage where the product gains popularity and sales grow. The company’s focus shifts to expanding distribution and maximizing market share.
- Maturity is the stage where the product reaches its peak sales. At this stage, the company focuses on maintaining market share and defending against competitors.
- Decline: This is when sales decline due to market saturation, new product competition, or changing consumer preferences. The company may consider reducing marketing efforts or discontinuing the product.
The PLC is a useful tool for businesses to understand the different stages of a product’s life and develop appropriate marketing strategies for each stage. For example, a company in the introduction stage of the PLC would focus on creating awareness and generating interest. In contrast, a company in the maturity stage would focus on maintaining market share and defending against competitors.
Key Trends Shaping the PLC in 2025
Several key trends are expected to shape the PLC in the years leading up to 2025, including:
- Accelerated product development cycles: The pace of product development is accelerating due to factors such as technological advancements and increased competition. This means that products are reaching the market faster than ever, and their lifecycles are becoming shorter.
- Increased consumer demand for personalization: Consumers increasingly demand personalized products and experiences. This pressures companies to develop products tailored to individual needs and preferences.
- The rise of e-commerce: E-commerce is rapidly growing and significantly impacts the PLC. E-commerce allows companies to reach a wider audience and sell products more quickly and efficiently.
- The increasing importance of sustainability: Consumers are becoming more aware of the environmental impact of their purchases, driving demand for sustainable products and packaging.
Implications for Businesses
These trends have several implications for businesses, including:
- The need for a more agile approach to product development: Companies need to be able to develop and launch products quickly and efficiently to stay ahead of the competition.
- The need to collect and analyze customer data: Companies need to collect and analyze customer data to develop personalized products and experiences.
- The need to invest in e-commerce capabilities: Companies need to invest in e-commerce capabilities to reach a wider audience and sell products more quickly and efficiently.
- The need to adopt sustainable practices: Companies need to adopt sustainable practices to meet the demands of environmentally conscious consumers.
Companies that can adapt to these trends will be well-positioned to succeed in the years to come.
Additional Considerations
In addition to the trends discussed above, businesses should also consider the following when developing their product lifecycle strategies:
- The unique characteristics of their industry and target market: The PLC can vary depending on the industry and target market. For example, the PLC for a fashion product is typically shorter than the PLC for a medical device.
- The company’s resources and capabilities: Companies must consider their resources and capabilities when developing product lifecycle strategies. For example, a company with limited resources may not be able to develop a product with a long lifecycle.
- The company’s competitive landscape: Companies must understand their competitive landscape when developing product lifecycle strategies. For example, a company facing stiff competition may need to develop products with shorter lifecycles to maintain market share.
By carefully considering these factors, businesses can develop effective product lifecycle strategies to help them achieve their goals.
Product Life Cycle Analysis
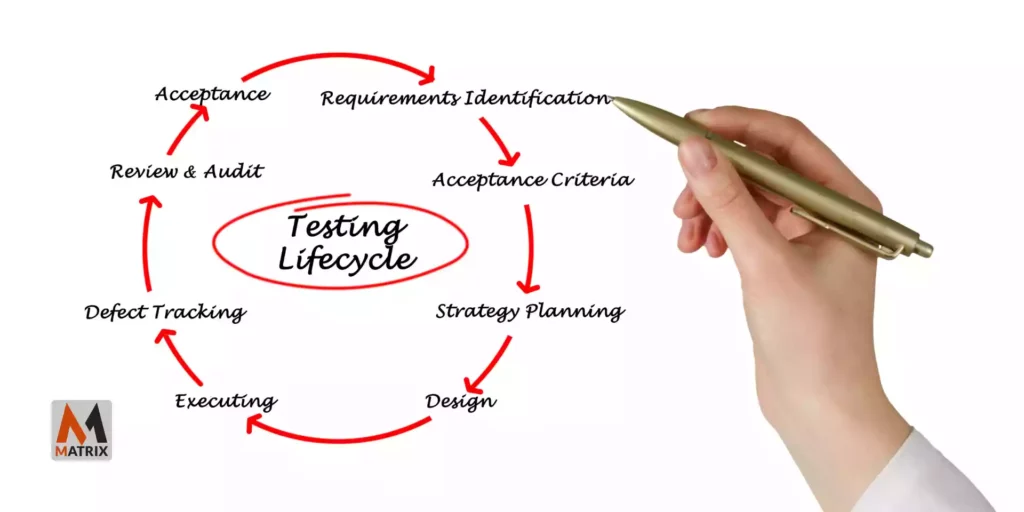
The product life cycle has several major stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline.
The important strategic issues in product life cycle analysis include:
- Determining the length and rate of change of the product lifecycle.
- Identify the current product life stage and select the product strategy corresponding to that stage.
- Anticipating strategic threats and finding opportunities for changing and extending the product life cycle.
Rate of Change in product life cycle management
Many products’ life cycles are becoming shorter. Microbrands like Casper Mattresses and Kylie Cosmetics are popping up daily and have become overnight successes. Of course, the length of the life cycle stages for particular products varies widely.
Determining the rate of change in the product life cycle is important. Marketing management must adjust its marketing strategy to correspond to the changing conditions.
For example, the product life cycle for computers is relatively short. In a few years, the product moved from its introduction into the growth stage and is now moving toward maturity.
Fast movement through the product life cycle also necessitates altering the cycle and/or introducing new products. In short, a rapidly changing product life cycle requires modifying marketing strategies in a dynamic environment.
Stages and Strategy Identification – product life cycle management
Now, we focus on the product life cycle (PLC). The product life cycle portrays distinct stages in the sales history of a product. Different opportunities and problems concerning marketing strategy and profit potential correspond to these stages. Companies can formulate better marketing plans by identifying a product’s stage or may be headed toward.
The product’s life cycle stage has implications for all aspects of targeting and positioning. Analyzing strategies for different situations, including the product life cycle stage, is critical.
The product’s life cycle stage has implications for all aspects of targeting and positioning. Each stage can define strategy zones as the product moves through the PLC.
The strategy guidelines indicate the changing focus of marketing strategy over the product life cycle.
It is not always clear where our product is positioned in its product life cycle at a specific time. Analysis of the growth rate, sales trends, time since introduction, the intensity of competition, pricing strategies, and end competitor entry or exit information is useful in positioning analysis. Free HubSpot CMS Tools
Identifying when a product has moved from growth to maturity is more difficult than determining other stage positions. Analyzing industry structure and competition is also important in estimating maturity.
Product Life Cycle Planning Model
Predicting a product’s sales revenue and identifying the factors that influence the shape and amplitude of the volume projections are important. A product life cycle model is used for short—and long-range planning for B2B and B2C businesses.
The model was designed to evaluate new product development projects. Estimating the timing and magnitude of turning points of a successful product introduction is perfect for this model. This modeling approach also appears useful for predicting an existing product’s life cycle.
The product life cycle model determines sales volume by combining original purchases and replacement estimates. Original purchases are forecasted using three predictor variables:
- Consumer need and product life cycle management
- Number of competitors
- Amount of advertising and promotional effort
- Social activity
- Digital competitive signals
Replacement estimates are a function of the products:
- Useful life, the percentage of owners who will replace it
- The trade-off of repair versus replacement
- Or the level of the initial purchases.
The validity test of the model predictions against actual product life cycles indicates a close correspondence between product life cycle shapes.
Product Portfolio Analysis

The strategic analysis of the product portfolio determines whether each product meets marketing management’s minimum performance criteria.
What is product life cycle management (PLCM)? PLCM is a process companies use to manage their products throughout their life cycles.
This includes anticipating new product attributes the market wants, finding new customer value benefits, and developing creative marketing strategies. PLCM also involves monitoring product performance and changing customer needs and preferences.
The product’s strengths and weaknesses relative to other products in the portfolio are also reviewed. The grid method can be used to compare products.
Portfolio grids show the differences among products.
An analysis of performance factors may include the following:
- Sales fluctuations and product life cycle management
- Profit contribution
- Barriers to entry
- The extent of capacity utilization
- The nature of technology
- Responsiveness of sales to price, promotional activities, service levels, and other influences
- Alternative production and process opportunities
- Environmental considerations
Several of these factors may be included in the product life cycle analysis. The analysis can also compare competing brands of a particular product.
This analysis may be useful when brands target different market segments. However, the grid’s market attractiveness dimensions will be constant across all brands targeting the market.
Positioning Analysis
Perceptual Maps offer powerful analysis tools for assessing products. They are developed by obtaining preference information on a set of competing brands or companies from a sample of buyers. Various product attributes are used, and the results are summarized in a two-dimensional preference map.
Product life cycle management software comes in handy here. AI product life cycle management is modern marketing.
Competitive mapping analysis offers useful guidelines for strategic product positioning. The analysis can relate buyer preferences to brands and indicate possible brand repositioning options.
Analyzing preference maps may identify new product opportunities. Positioning studies can measure the impact of repositioning strategies.
Other Product Analysis Methods
Other product analysis methods include research studies that identify the relative importance of product selection criteria to buyers and rate brands against these criteria. These techniques are useful in indicating brand strengths and weaknesses.
Industry analysts (e.g., IDC and Gartner) and trade publications publish market share and other brand performance data. Product rating services, such as those offered by Consumer Reports, also provide useful evaluations of brands and products.
Online reviews can tell a lot about a product. Websites like G2Crowd and Capterra are great resources I use all the time.
Wrap Up on product life cycle management and analysis

Products and markets have life cycles that call for changing marketing strategies. Every new product follows a product life cycle. It passes through the stages of emergence, accelerating growth phase, declining growth, maturity, and decline.
Companies must try to anticipate the market’s desire for new product attributes. Those who introduce new products earn profits.
Customer value benefits from searching for new attributes based on empirical work, intuition, or needs hierarchy reasoning.
Successful marketing comes through creativity, visualizing the market’s evolutionary potential. This is where product portfolio analysis can be used for the product life cycle.
General FAQs about product life cycle analysis
What are the different stages of the product life cycle?

The different stages of the product life cycle are as follows: (1) Emergence, (2) Accelerating growth, and (3) declining growth.
How can businesses use product life cycle analysis?

Businesses can use product life cycle analysis to understand when their products are in which cycle stage and make better decisions about their marketing strategies. They can also use it to identify new opportunities for their products.
What is perceptual mapping, and how can it be used?

Perceptual mapping is a technique that helps businesses understand how their customers view their products. It does this by mapping customer preferences onto different brands or companies. This can be useful for assessing different brands’ strengths and weaknesses and identifying possible brand repositioning options.
What is positioning analysis, and how can it be used?

Positioning analysis is a technique that helps businesses understand how their customers view their products. It does this by mapping customer preferences onto different brands or companies. This can be useful for assessing different brands’ strengths and weaknesses and identifying possible brand repositioning options.