Multiagent Systems for Marketing Strategy
Learn How Multiagent Systems for Marketing Strategy Saved Emily’s Career as a CMO
Emily Anderson, the Chief Marketing Officer at ReviveTech, was under intense pressure. Her CEO, board members, and entire team demanded better marketing performance, faster campaign turnarounds, and, most importantly, a significant return on investment.
It wasn’t that Emily wasn’t good at her job; on the contrary, she’d built a stellar career based on innovation and creativity. However, as ReviveTech grew, its marketing challenges grew even faster, and traditional strategies weren’t keeping pace.
Every day, Emily struggled with growing expectations, competitive pressures, and an endless to-do list that exhausted her without the concrete results she needed. ReviveTech’s target audience was evolving, the competition was intense, and her team was overwhelmed with data they barely had time to process.
One afternoon, after another meeting with the board questioning last quarter’s ROI, Emily was approached by Mark, her friend and the company’s VP of Product. Mark had seen Emily’s struggle and empathized with her stress.
“Emily, have you ever heard of Multiagent Systems?” he asked.
She sighed, “I’ve heard the term, but honestly, I don’t fully understand how it would help in marketing. Isn’t MAS something for engineers and robotics?”
Mark shook his head. “Not anymore. MAS can bring together multiple AI agents that collaborate, each handling specific marketing functions like product management, brand strategy, and content.
It’s like having a virtual team working 24/7, helping you manage data, create content, and optimize the customer journey.”
Emily was intrigued. She’d always been open to tech innovations but had never considered MAS a solution to her marketing woes.
After some research and a detailed presentation from a consultant, Emily decided to pitch MAS to the board, highlighting how it could streamline their efforts, reduce costs, and ultimately increase ROI. She wasn’t entirely sure how it would pan out, but she felt it was worth taking.
Implementing MAS at ReviveTech

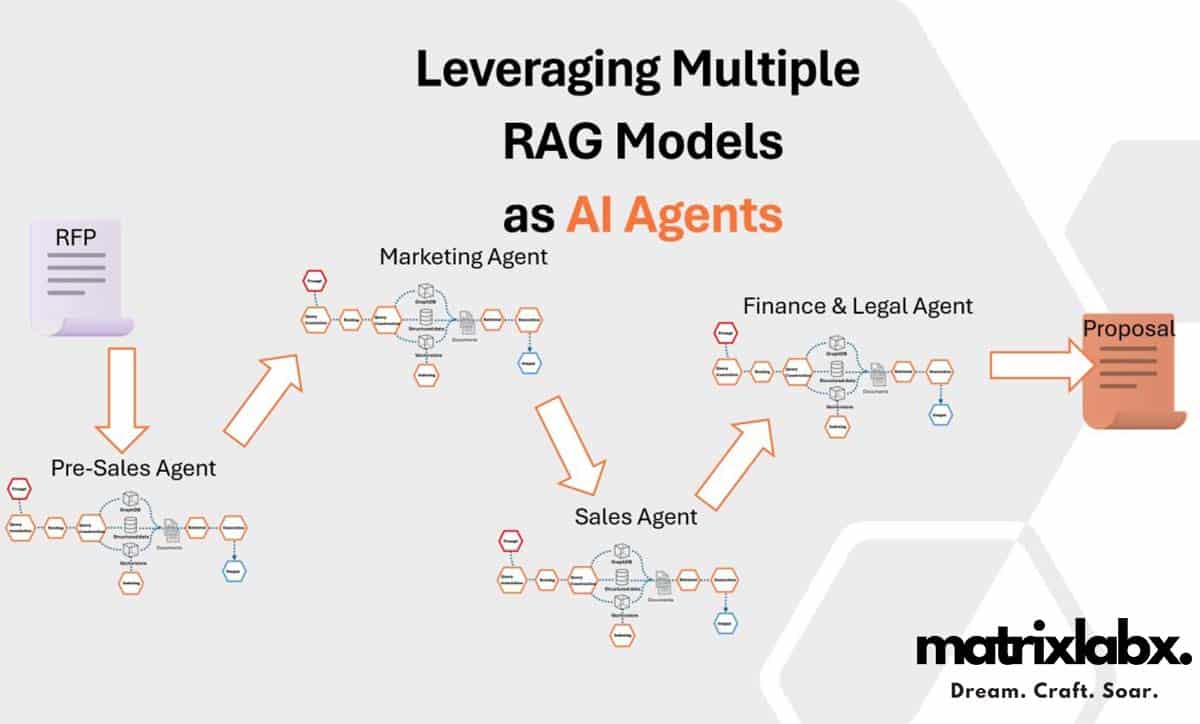
Emily’s first task was integrating three specific agents: AIProdPad, AIBrandPad, and AIContentPad. Each was designed to focus on a critical aspect of marketing:
- AIProdPad analyzed product data and customer feedback to help Emily understand what features were resonating with the audience. This gave Emily real-time insights into what people valued most in ReviveTech’s products.
- AIBrandPad monitored brand perception across channels, identifying trends and sentiment shifts. It informed Emily’s team when to emphasize particular values or adjust their messaging to align with audience expectations.
- AIContentPad generated content ideas, drafted marketing copy, and personalized messaging for different audience segments. It even adapted content based on real-time engagement metrics.
Initially, Emily’s team was skeptical. They were used to creating strategies and content through human creativity and weren’t sure if they could trust these “intelligent agents” to understand the nuances of marketing. But as they began using the system, they realized how much time it saved.
The distinction between multi-agent systems (MAS) and AI agentic systems lies in their design, functionality, and level of autonomy. While both are based on the concept of “agents”—independent, goal-driven entities—there are key differences in structure, purpose, and technological complexity.
1. Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
- Definition: Multi-agent systems are composed of multiple agents working together to solve complex problems or achieve shared objectives. Each agent operates independently but collaborates and communicates with others in the system.
- Purpose: MAS is primarily focused on creating a network of agents that can collectively tackle complex tasks. The goal is often to distribute problem-solving efforts among agents, allowing them to work simultaneously to increase efficiency and handle distributed or large-scale problems.
- Level of Autonomy: MAS agents typically have limited autonomy and follow predefined rules. They are designed to communicate and cooperate based on established protocols but are usually programmed with fixed behaviors.
- Example: In a warehouse management system, multiple agents could be responsible for different tasks (e.g., organizing inventory, tracking shipments, coordinating delivery). These agents operate within a shared environment, each performing a specific role to optimize the workflow.
2. AI Agentic Systems
- Definition: AI agentic systems are built on more advanced AI algorithms and are often designed with more autonomy, adaptability, and intelligence. An AI agentic system doesn’t just follow predefined rules; it learns from data, adapts to changing conditions, and can make decisions independently.
- Purpose: AI agentic systems are focused on creating intelligent agents that can autonomously learn, make decisions, and potentially operate in complex, dynamic environments without human intervention. They’re capable of achieving individual goals while also contributing to larger objectives.
- Level of Autonomy: These systems feature higher levels of autonomy and adaptability. AI agents can modify their behavior based on new data or feedback, improving their performance and decision-making over time.
- Example: AIProdPad or AIContentPad, products from MatrixLabX, are examples of AI agentic systems. These agents adapt their strategies based on user engagement metrics, market trends, and real-time data. They continuously improve their ability to target the right audiences, optimize campaigns, and personalize content autonomously.
Key Differences
| Aspect | Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) | AI Agentic Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Complexity | Designed for task-specific coordination | Built for high autonomy, learning, and adaptation |
| Goal | Coordination and cooperation among agents | Autonomous decision-making and self-improvement |
| Adaptability | Limited adaptability; follows preset protocols | Highly adaptive, learns from data and environment |
| Application | Distributed problem-solving | Dynamic problem-solving with intelligent behavior |
| Examples | Logistics management, resource allocation | Autonomous marketing, personalization, adaptive content management |
In essence, while MAS focuses on agent collaboration with limited adaptability, AI agentic systems prioritize autonomy, intelligence, and the ability to evolve independently—making them well-suited for more complex, dynamic applications like personalized marketing, predictive analytics, and real-time decision-making.
MAS at Work: The Results Speak for Themselves
The MAS agents operated smoothly within a month, transforming the team’s work. Emily quickly saw improvements that felt almost magical.
The ROI jumped over with MatrixLabX’s Domain-Specific AI Agents, a groundbreaking collaborative AI framework that revolutionizes marketing with advanced autonomous units of expertise.
Designed specifically for marketing departments, these specialized AI agents represent a significant leap forward. They combine AI Collaboration, Metacognition, Specialized Agents, and Neuro-Symbolic Reasoning to achieve next-level intelligence. This unique architecture allows AI to operate with enhanced self-awareness, specialized skillsets, and human-like reasoning, transforming how marketing teams achieve their goals.
1. Efficiency and Faster Campaign Turnarounds
Content production was previously a bottleneck. Her team was often bogged down in brainstorming sessions and editing cycles.
With AIContentPad, campaign content was generated rapidly, personalized to specific audience segments, and optimized based on previous performance data. What used to take weeks was now done in days, even hours.
AIProdPad provided product insights that helped her team target specific product benefits in their marketing, while AIBrandPad alerted them of shifts in sentiment so they could adjust their messaging instantly. These agents made the team faster and more responsive than Emily had ever imagined.
2. Data-Driven Personalization at Scale
One of the standout benefits was how MAS enabled Emily to personalize marketing at scale. AIContentPad was continuously learning and studying engagement metrics and customer behavior patterns.
This meant the system could craft highly personalized content for different customer personas without her team spending hours on segmentation.
Each message felt tailored, improving engagement rates and contributing to a more positive brand image.
3. Improved ROI Through Smarter Allocation
The most exciting result for Emily was the measurable improvement in ROI. With MAS, she could better allocate budget and resources.
Studies show that integrating artificial intelligence can drive impressive returns for marketers, with ROI estimates ranging from 110% to 350% — and some companies even report up to 8 times their investment. The impact, however, depends on how well AI aligns with your unique goals and needs. To achieve maximum value, consider evaluating how AI fits into your specific business case to get a more tailored and realistic projection.
AIProdPad recommended which product features to emphasize based on customer feedback, while AIBrandPad’s insights enabled Emily to refine her branding strategy continuously.
Together, these insights significantly reduced wasted spending and efficiently used her budget.
Marketing initiatives that were previously risky became data-backed decisions, and her campaigns yielded higher returns than any of her traditional methods had in the past.
Surpassing Expectations and Saving Her Job

Within three months, ReviveTech’s marketing KPIs were at an all-time high. Revenue from new customers had increased by 20%, engagement rates on marketing campaigns had doubled, and, most impressively, customer satisfaction scores were through the roof. Emily’s board, initially skeptical, was now fully on board with MAS, praising her for the foresight to adopt such an innovative approach.
Her CEO, who had once hinted that her position might be in jeopardy, congratulated her personally. “Emily,” he said in a meeting, “you’ve not only saved your department; you’ve redefined how we approach marketing entirely.”
Her team, initially wary of MAS, was relieved to have AI agents handle the heavy data lifting. They could focus on the creative and strategic elements of marketing—things they enjoyed and excelled at—while leaving the grunt work to the AI.
Lessons Learned: Emily’s Takeaways for Other CMOs
Looking back, Emily felt like a trailblazer. She realized that MAS wasn’t just a technological upgrade but a complete shift in how marketing could function.
Her experience taught her several valuable lessons, which she now shares with other CMOs:
- Don’t Be Afraid to Innovate: MAS initially seemed intimidating, but embracing it was her most successful decision.
- Trust the Data, But Add a Human Touch: MAS provided Emily with reliable, data-driven insights, but her team’s creative vision remained crucial in crafting messages that resonated emotionally.
- Focus on Personalization: MAS allowed her to personalize marketing messages on a level she never thought possible, which translated directly into improved ROI and brand loyalty.
- Save Time for Strategy: By automating routine tasks, Emily and her team could focus on strategy and innovation, where they could make the most significant impact.
- Continual Learning and Adapting: MAS isn’t static; it evolves based on the data it processes. Keeping up with these insights allowed her to remain agile and responsive.
A Brighter Future with Multiagent Systems
With MAS, Emily turned ReviveTech’s marketing department into a responsive, data-driven powerhouse. Instead of spending days on reports, she now had real-time insights. Her team, once bogged down by data and repetitive tasks, was reinvigorated, focusing on creative strategies and big-picture ideas.
As Emily reflected on the transformation, she knew MAS had saved her job.
But more than that, it had redefined her marketing approach, empowering her to lead ReviveTech into a future of innovation, personalization, and sustained growth.
Thanks to MAS, Emily went from merely surviving to thriving as a CMO.
1. Introduction to Multiagent Systems (MAS)
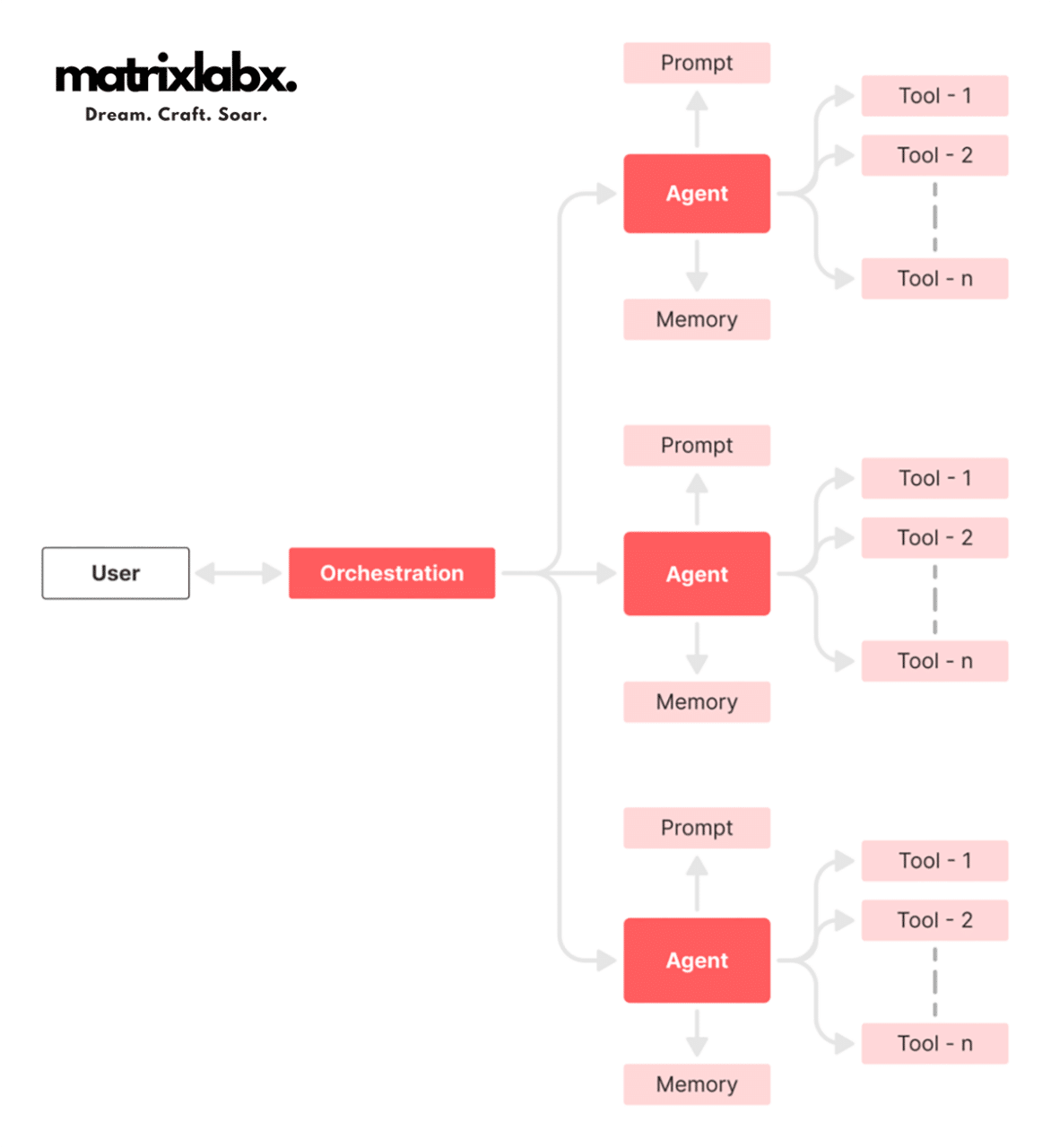
Definition and Overview: What Are Multiagent Systems?
Multiagent Systems (MAS) represent a significant advancement in artificial intelligence (AI), in which multiple autonomous AI agents work collectively to achieve complex objectives.
Each agent can make decisions independently yet collaboratively in a MAS, enhancing task efficiency and complexity management.
Agents can be deployed across various organizational functions, communicating and sharing data to accomplish collective goals that would otherwise be time-intensive or challenging for single-agent systems.
Importance for Modern CMOs
For Chief Marketing Officers (CMOs), the rapid evolution of AI and data-centric strategies has made it critical to adopt intelligent systems that can support dynamic market demands.
MAS is particularly relevant as it offers scalability and adaptability, empowering CMOs to respond swiftly to shifting customer preferences, emerging trends, and competitive pressures.
MAS enables the seamless orchestration of tasks across product management, brand strategy, and content marketing, significantly enhancing a CMO’s ability to foster growth and innovation in a fast-paced digital environment.
Key Concepts: Understanding Agents, Autonomy, Cooperation, and Task Specialization in MAS
In an MAS, each agent operates autonomously while maintaining the capability to interact with other agents and the environment. This autonomy means agents can make independent decisions based on data and predefined rules.
Additionally, cooperation among agents is critical in MAS, where agents share information and resources to achieve shared goals effectively.
MAS typically supports task specialization, with each agent proficient in specific functions—optimizing product performance, managing brand image, or creating content.
This specialization within MAS allows companies to build agile systems capable of rapid, intelligent decision-making.
2. Components of Multiagent Systems in the Context of Marketing AI
Autonomous AI Agents Explained
- AIProdPad: This AI agent focuses on product management, analyzing product performance, market trends, and customer feedback to guide product development and optimization.
- AIBrandPad: Responsible for brand management, AIBrandPad gathers and analyzes brand-related data, helping organizations maintain consistent brand identity, adapt to market changes, and enhance brand perception.
- AIContentPad: AIContentPad excels in content marketing, generating tailored content, tracking content performance, and adjusting strategies to maximize engagement and conversion.
Each agent contributes distinct expertise, making MAS a powerful tool for comprehensive marketing efforts.
Independent Yet Collaborative
In an MAS, the agents operate independently within their areas of expertise while maintaining a collaborative relationship.
For instance, AIProdPad could identify new product features based on market data, while AIBrandPad aligns branding to emphasize these features.
Meanwhile, AIContentPad generates content to market the product effectively.
This independence allows each agent to execute tasks with minimal interference, while collaboration among agents ensures alignment with the organization’s strategic goals.
Data Sharing and Communication
A critical aspect of MAS is agents’ real-time ability to share data and insights.
This continuous data exchange facilitates seamless collaboration, allowing each agent to make data-informed decisions while considering the broader business context.
Data sharing in MAS minimizes silos, ensuring that all agents have access to the most up-to-date information.
3. Benefits of MAS for Modern Businesses

Scalability
One of MAS’s key benefits is scalability. As the number of agents in the system increases, organizations can expand their operations without proportionally increasing human resources or infrastructure.
For CMOs, this scalability allows marketing activities to be adjusted quickly, accommodating everything from small campaigns to large-scale brand initiatives.
Adaptability
MAS enables a level of adaptability that single-agent systems cannot achieve. Multiagent collaboration allows for real-time responsiveness to changing market dynamics.
When customer behaviors shift or new competitors emerge, MAS can quickly adjust marketing strategies, ensuring the organization remains agile.
Performance and Efficiency
In MAS, multiple agents can handle various tasks concurrently, significantly improving performance and efficiency.
By dividing work among specialized agents, tasks are completed faster, and bottlenecks are minimized.
MAS’s efficiency is particularly beneficial in data-heavy environments, where the system can analyze vast data sets more efficiently than human teams or single-agent systems.
4. MAS Architectures and Structural Design
Common MAS Structures
- Hierarchical Structures: This architecture involves a top-down approach where a primary agent oversees and coordinates sub-agents. Hierarchical structures are useful for ensuring command and control, as they allow for a structured flow of information and clear task delegation.
- Decentralized Structures: In decentralized structures, each agent operates with greater autonomy, making independent decisions based on local data and interactions with other agents. This flexibility enables faster adaptation to environmental changes, which is ideal for dynamic, rapidly evolving industries like marketing.
Behavioral Models in MAS
- Flocking behavior is a coordinated movement among agents that mimics how birds or fish move in groups. In MAS, this behavior allows agents to stay aligned and avoid obstacles collectively, which is useful for maintaining cohesion in complex tasks.
- Swarming: Swarming behavior involves agents working in close cooperation without a centralized controller, which is ideal for handling dynamic, complex challenges. Swarming allows MAS to adapt fluidly to unexpected changes, such as spikes in customer demand.
Choosing the Right Architecture
Selecting the appropriate MAS architecture depends on the organization’s goals and the complexity of the tasks.
A hierarchical structure may suit highly coordinated, controlled operations, while decentralized structures may benefit organizations requiring rapid adaptability.
5. Applications of MAS Across Various Fields

Marketing and Sales
- Personalization at Scale: MAS enables precise audience segmentation, allowing for highly personalized messaging. Agents can analyze customer behavior data, predict preferences, and craft individualized campaigns.
- Customer Journey Optimization: With MAS, marketers can track and adjust the journey in real-time, ensuring customers receive timely and relevant messaging.
- Domain-Specific AI Agents for Marketing Departments: Autonomous Units of Expertise
Healthcare
- Enhanced Diagnostics: MAS can collaborate to analyze medical data, cross-referencing with patient histories to improve diagnostic accuracy.
- Patient Care Coordination: Agents can coordinate care across different departments, ensuring seamless communication and optimal patient outcomes.
Manufacturing Firms
- Smart Production Lines: MAS facilitates smart manufacturing, with agents controlling IoT-enabled devices on production lines, streamlining operations and improving quality.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: MAS enables real-time tracking and adjustment of supply chain operations, ensuring timely delivery and inventory management.
- AI Branch Models for Marketing Manufacturing Companies with AI Agentic Systems
Technology Companies
- Product Development: Agents within MAS can collaborate on R&D, combining data analysis, prototyping, and testing to accelerate innovation.
- Customer Support Automation: MAS allows for responsive, intelligent customer support, using data insights to provide personalized assistance.
6. Challenges in MAS Implementation and Coordination

Inter-Agent Communication
Effective MAS requires seamless communication among agents to prevent data loss and ensure decisions are based on accurate information.
Inter-agent communication involves synchronizing data exchange protocols, which can become complex in large-scale systems.
Complex System Management
System managers can face challenges in overseeing multiple agents with independent decision-making abilities.
Coordination becomes essential, especially when balancing short-term tasks with long-term objectives.
Data Privacy and Security
As MAS involves sharing potentially sensitive data among agents, protecting this data from breaches and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations is critical.
Resource Allocation
MAS can be resource-intensive, with each agent requiring processing power and data storage.
Careful planning is necessary to allocate resources efficiently without overwhelming the system.
7. Future Implications for CMOs Using MAS
Competitive Advantage
CMOs who adopt MAS can gain a competitive edge through data-driven insights and faster response times.
MAS’s ability to deliver timely, targeted messaging can help brands stand out in a crowded marketplace.
Strategic Agility
MAS’s adaptability allows CMOs to adjust strategies in real time based on market trends.
Its agility means CMOs can seamlessly shift focus to align with customer sentiment or competitive changes.
Customer-Centric Innovation
MAS allows brands to anticipate customer needs and deliver relevant, personalized experiences.
By analyzing customer feedback and predicting preferences, brands can offer more targeted, satisfying experiences, fostering loyalty.
Intelligent AI Agentic Systems
The Next Frontier of Generative AI: Agentic Systems
These systems function as autonomous digital colleagues, able to plan, reason, and execute complex tasks with minimal human intervention. Their capabilities allow them to transform from helpful assistants into proactive decision-makers and core contributors in business environments.

8. Conclusion

Summary of Key Points
Multiagent Systems represent a transformative shift in AI, offering new ways for CMOs to scale marketing operations, adapt to changing conditions, and improve efficiency.
With agents specializing in product management, brand strategy, and content creation, MAS offers a holistic approach to modern marketing.
Action Steps for CMOs
To start integrating MAS:
- Evaluate Needs: Identify which aspects of marketing would benefit from MAS.
- Define Roles for Agents: Determine the functions of each agent to meet specific marketing goals.
- Plan for Scalability: Ensure the system can grow with your marketing strategy.
- Invest in Data Security: Implement security measures to protect data privacy.
By embracing MAS, CMOs can drive their organizations toward more agile, customer-centric, and innovative marketing strategies.

