Product Vision Examples Can Supercharge Your Success.
Learn About How to Use Product Vision Examples to Supercharge Your Success.
Learn how product vision examples can help you speed up your product launch.
Quick stats about the vision statement.
- 64% of product leaders say a clear vision statement increases employee productivity. (Source: Product Alliance Survey, 2023) Yet, only 42% report having a written vision statement readily accessible to their team. (Source: Airfocus, 2023) This suggests a disconnect between understanding the value of a clear vision and actively implementing it.
- Products with specific, measurable vision statements are 54% more likely to achieve their goals. (Source: Gartner Product Management Survey, 2022) This highlights the importance of setting concrete targets within the vision, not just aspirational statements.
Challenges in Product Management and Product Vision Examples
Today’s Marketing managers face various challenges, impacting their ability to drive their brand’s marketing efforts effectively. Here’s a list of common pains and desires that marketing managers often experience:
- Team Experience and Staffing Issues: As the scope of Internet marketing expands, marketing managers often grapple with teams that may need more key skills or be understaffed in crucial areas like conversion rate optimization or technical SEO. A significant challenge is balancing a team with diverse specialties while avoiding being overburdened.
- Interpreting Marketing Data: Understanding and accurately interpreting marketing report data is essential. The ever-evolving marketing vocabulary and the depth of data available can make it challenging for managers to analyze and leverage insights for strategic decisions confidently.
- Managing Multi-Channel Marketing Strategies: Executing a comprehensive plan across multiple channels like social media, email, and search engines requires an in-depth understanding of the target audience and effective coordination of messaging and branding across platforms.
- Creating Engaging Content: Producing content that resonates with the target audience while being visually appealing and optimized for search engines and social media is complex. It involves a deep understanding of the audience’s needs and preferences.
- Building Brand Awareness: Developing and promoting a brand that is recognizable and appealing to the target audience while ensuring consistency in messaging across all channels is a major focus for marketing managers.
- Proving ROI of Marketing Activities: Demonstrating the return on investment for marketing initiatives is crucial. This involves setting clear goals, using data and analytics, calculating customer acquisition costs, and regularly providing updates to stakeholders.
- Communication Breakdown in Marketing Departments: Ensuring effective communication within the marketing team, especially regarding campaign results and strategy improvements, is key. A lack of comprehensive reporting can lead to strategic misalignment and inefficiency.
- Executive Interaction: Marketing managers often need help communicating effectively with executive management, especially in conveying marketing campaigns’ success and strategic direction.
- Closing the Loop with the Sales Team: Aligning marketing strategies with sales objectives and ensuring both departments work cohesively towards common goals is a significant challenge.
Understanding these challenges is the first step in developing strategies to address them, enhancing the effectiveness of marketing efforts and overall business success.
Trends in AI product management
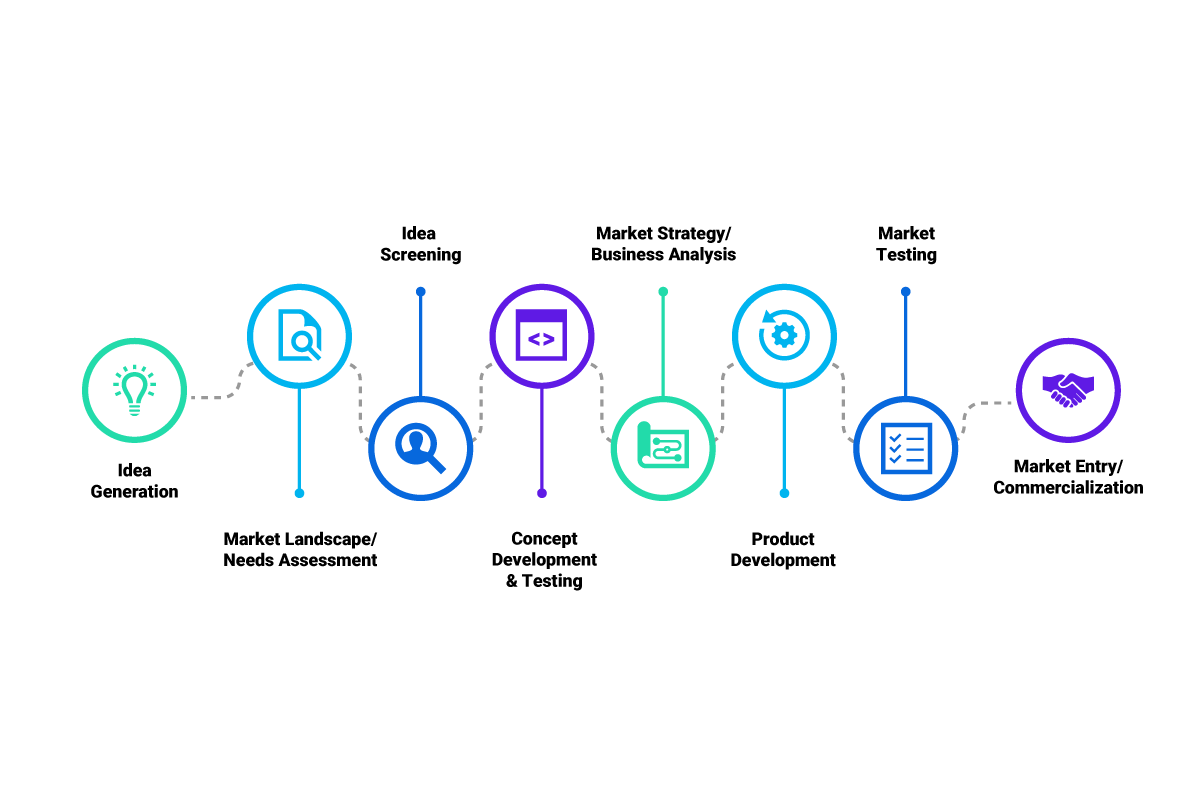
How to craft effective product vision statements and provide examples from successful companies.
Importance of Product Vision:
Product vision is crucial as it provides strategic direction, inspires and motivates teams, aligns different organizational functions, and aids in prioritization. It sets the long-term goal and guides decision-making to ensure consistency with this direction.
A product vision is more than just words; it is a guide that gives teams a common understanding of their goals, helping increase productivity and achieve objectives faster. It also aids in feature prioritization, road mapping, and backlog refinement, thus shortening the time to market.
Creating a Product Vision:
A product vision should be co-created with relevant stakeholders and key team members. It’s recommended to involve the team in brainstorming and to use techniques like writing and editing vision statements collaboratively or using empathy maps to gain deeper user understanding.
The product vision statement should be inspiring, shared, concise, ambitious, and enduring. A typical template for crafting a vision statement involves identifying the target customer, their needs, the product’s unique selling points, and its differentiation from competitors.
Differences Between Product Vision, Mission, and Strategy:
A product vision statement is futuristic and strategic, defining the long-term value the product aims to provide. In contrast, a mission statement is about the current objectives of the product and how it achieves them.
The vision drives the product strategy, which outlines what needs to be done for the product to reach its vision.
Examples of Effective Product Vision Statements:
Notable examples include Sonos (“Fill every home with music”), Google (“To provide access to the world’s information with one click”), Instagram (“To capture and share the world’s moments”), Uber (“Evolving the way the world moves”), and LinkedIn (“To connect the world’s professionals and make them more productive and successful”).
Other examples, like Apple’s iPod (“1000 songs in your pocket”), showcase successful product visions’ clarity and aspirational nature.
These discussions emphasize that a powerful product vision is fundamental for guiding a product’s development and ensuring its success in the market.
Expanding upon the central ideas of an article titled “Product Vision Examples,” it’s important to delve into the significance of a compelling product vision in guiding a product’s journey from conception to market success. A well-crafted product vision is a north star for product development, aligning all stakeholders and driving innovation.
1. Significance of a Clear Product Vision Statement:
- Strategic Alignment: A product vision aligns the efforts of various teams – from engineering to marketing – ensuring that everyone works towards a common goal. This alignment is crucial in maintaining a consistent product development trajectory.
- Inspiration and Motivation: An inspiring product vision galvanizes teams, fostering a sense of purpose and commitment. This can be seen in Apple’s vision for the iPod, “1000 songs in your pocket,” which communicated a transformative idea and motivated the team to achieve it.
2. Impact on Decision-Making and Innovation:
- Guiding Product Development: A robust product vision influences key decisions regarding feature prioritization, technological choices, and market positioning. For instance, Google’s vision to organize the world’s information made them focus on developing an efficient and comprehensive search engine.
- Fostering Innovation: A visionary goal encourages teams to think out of the box. Amazon’s vision of being the world’s most customer-centric company led to innovative practices like one-click purchasing and personalized recommendations.
3. Examples of Successful Product Visions:
- Tesla: Tesla’s vision of accelerating the world’s transition to sustainable energy has shaped its product strategy and revolutionized the automotive industry.
- Netflix: Starting with the vision to provide accessible entertainment, Netflix evolved its business model from DVD rentals to a streaming service, fundamentally changing how people consume media.
4. The Evolution of Product Visions:
- Adaptability to Market Changes: Successful product visions are adaptable. Microsoft’s shift from a vision focused on personal computing to a cloud-first, mobile-first approach is a prime example of adapting to changing market dynamics.
- Long-Term Orientation: The best product visions are not just about immediate goals but encapsulate a long-term aspiration. LinkedIn’s vision to connect professionals globally has kept it focused on network expansion and value-added services over time.
5. Crafting an Effective Product Vision:
- Involving Stakeholders: Engaging various stakeholders in the vision creation process ensures a comprehensive understanding of customer needs, market trends, and potential challenges.
- Simplicity and Clarity: A product vision should be easily understandable and memorable. It needs to succinctly convey the essence of what the product aims to achieve.
A product vision is a fundamental aspect of product management that drives strategic alignment, inspires innovation, and guides decision-making.
By examining successful examples and understanding the key components of an effective vision, companies can craft visions that resonate with their teams and significantly impact the market.
The trending topics around product vision examples for 2024 encompass a range of innovations and strategic shifts in product management, branding, and marketing:
- Rapid Prototyping and Feedback Cycles: The advancement of 3D printing technology expedites product development. This leads to faster feedback and iteration cycles, necessitating continuous innovation to keep up with shorter product life cycles.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: IoT is revolutionizing product management by increasing the number of interconnected devices. This surge in IoT devices means products are increasingly designed with built-in connectivity and data collection capabilities, enhancing customer experiences and creating new business models like product-as-a-service.
- AI in Product Management: AI is automating various aspects of product management, including data analysis, decision-making, and personalization of user experience. AI-powered tools are emerging to streamline processes and enhance decision-making in product management.
- Data Analytics as a Decision-making Tool: Data analytics is increasingly vital in product management for informing product strategies, guiding design and development, planning product launches, and monitoring product performance.
- Emotional Intelligence in Product Management: Emotional intelligence is becoming a crucial skill in product management. It aids in understanding customer needs, fostering team collaboration, and managing complex stakeholder relationships.
- Cybersecurity Considerations: Cybersecurity is becoming a critical aspect of product management, necessitating security built into products from the beginning and continuous monitoring for potential threats.
- Hybrid Project Management: This approach combines elements of different project management methodologies, such as Waterfall, Agile, and Scrum, providing flexibility and adaptability in complex and dynamic project environments.
- Authentic Brand Engagement: Authentic storytelling and demonstrating empathy are crucial for brands to engage audiences genuinely and build trust.
- Polarization and Ethical Consumerism: Brands increasingly focus on aligning with consumer beliefs, which has given rise to “conservative” and “woke” branding strategies.
- Personalization in Marketing: Advanced AI and machine learning play pivotal roles in creating personalized consumer experiences.
- Emerging Branding Trends: Trends like hand-drawn branding elements, simple maximalism, cutouts in packaging, mascots for emotional connection, eco-friendly brand looks, and fun with fonts are shaping brand identities.
- Immersive Experiences: Technologies like VR and AR continue to grow in adoption, with brands exploring these to create differentiated customer experiences.
- Employee-driven Marketing: Brands increasingly leverage their employees as brand ambassadors, focusing on authenticity and cost efficiency.
- Brevity in Storytelling: Brands are adapting to the dwindling attention span of audiences by mastering concise storytelling using potent visuals and micro-content.
These trends highlight a move towards more integrated, authentic, and personalized product management and marketing approaches, emphasizing advanced technologies and a deep understanding of consumer behavior and expectations.

When looking to purchase a product management platform, individuals often encounter several common challenges:
- Balancing Multiple Demands and Priorities: Product managers typically juggle numerous tasks like strategy formulation, team coordination, and dealing with product development issues. This requires effective time management and prioritization skills.
- Establishing and Maintaining Product Focus: Maintaining focus on the original vision of the product while managing the influx of new ideas and features can be challenging. This involves resisting the temptation to add too many features and staying true to the core product value.
- Managing Product Launches: Product launches involve several moving parts and tight deadlines. Creating detailed launch plans and checklists can ensure smooth execution.
- Prioritizing New Features: Deciding which features to add to a product can be difficult. This requires a data-driven approach, considering customer needs and using product analytics tools for decision-making.
- Analyzing Product Data: Understanding and interpreting product data is crucial for informed decision-making. Utilizing analytics tools and enlisting the help of a data analyst can be beneficial.
- Collecting and Managing Customer Feedback: With various feedback channels, it’s essential to have a system in place to track and manage customer feedback effectively. Using customer feedback management tools can be very helpful in this regard.
- Product Adoption and Onboarding: Ensuring that users not only start using the product but also stick with it is crucial. Strategies like product tours, interactive walkthroughs, and maintaining a library of self-help resources can enhance user onboarding and retention.
- Product Roadmap Prioritization: Choosing what to focus on can be challenging without a universal measure of value. Setting clear metrics for prioritizing features and using customer feedback effectively are key strategies.
- Keeping Up with Deadlines: Managing both internal and external deadlines can be stressful. Using a product roadmap for task management, setting realistic goals, and conducting project retrospectives can help meet deadlines.
- Staying Updated on Product Changes: Continuously tracking customer experience metrics and feedback is vital for adapting the product to meet user needs.
These challenges can be mitigated through strategic planning, effective use of technology, and strong team collaboration. Solutions like Userback and other visual feedback platforms can be instrumental in managing these aspects efficiently.

